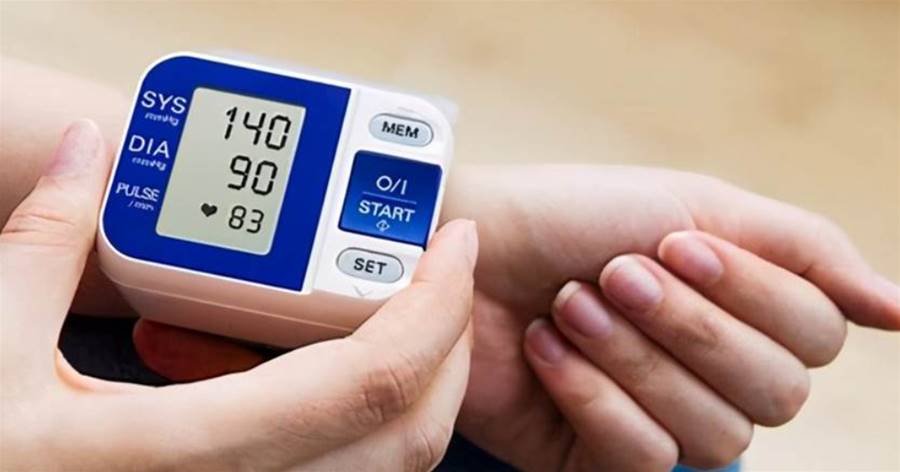
Why is hypertension becoming more prevalent?
1. Chronic Lack of Sleep: Chronic lack of sleep can accelerate the aging of blood vessels in young people, leading to hypertension. Poor sleep quality increases pressure on blood vessels and the heart, causing an increase in blood pressure and heart rate, making individuals more prone to developing hypertension.
2. High Salt Diet: With improved living standards, people pay more attention to taste and consume foods like hot pot, barbecue, and spicy food.
These foods often contain excessive amounts of salt, which contributes to hypertension. Therefore, it is recommended to eat lighter and healthier meals.

3. Obesity: Most hypertensive patients are overweight or obese. Controlling fat intake and exercising regularly are essential for managing hypertension.
4. Sedentary Lifestyle: People who spend long hours sitting without exercising are more likely to develop hypertension. Lack of physical activity leads to the accumulation of fat and cholesterol in the body, resulting in weight gain and an increased risk of high blood pressure.
Doctors advise people taking antihypertensive medication to avoid consuming certain foods:
1. Fatty Meat: Fatty meat contains high levels of fat and cholesterol, which can further raise blood pressure.
It is recommended that hypertensive patients consume lean meat instead.

2. Milk: Milk is nutritious and beneficial for calcium supplementation, but it can interact with antihypertensive drugs, causing dizziness and affecting their efficacy.
3. Grapefruit: Grapefruit's high vitamin content can boost metabolism and aid weight loss, but it can inhibit the efficacy of antihypertensive drugs.
It is not recommended for individuals taking such medication.
4. Strong Tea: The tannic acid in tea can react with medications, leading to precipitation and reduced efficacy. It is best to separate the consumption of tea and medication.

5. Oranges: Oranges are nutritious and rich in potassium, making them beneficial for those with potassium deficiency.
However, oranges can interact with antihypertensive drugs and inhibit their efficacy.



















