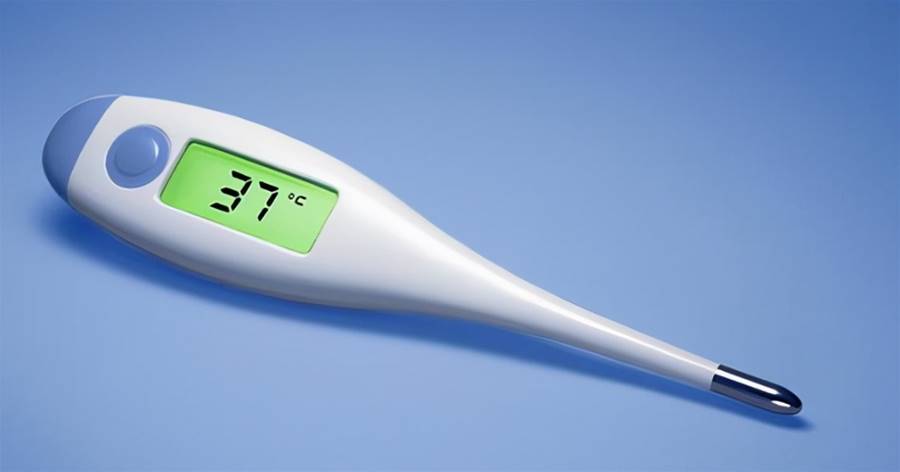
Some scientists suggest that for every 1°C decrease in body temperature, the immune response decreases by 30%. However, does this mean that higher body temperature leads to a stronger immune system?
Research has found a link between body temperature and basal metabolic rate. For every 1°C increase in body temperature, the basal metabolic rate increases by 13%.

When body temperature is high, blood flow is faster, allowing immune cells to respond quickly and eliminate pathogens. Conversely, when body temperature decreases, blood flow slows down, resulting in slower immune responses and failure to clear viruses in time, leading to diseases.

Therefore, it is important to approach the relationship between body temperature and immune response with rationality.
Whether it is a decrease or increase in body temperature, as long as it stays within a suitable range, it is considered normal.




















