Low potassium levels in the body can cause various symptoms and impact overall health. Potassium plays a crucial role in maintaining muscle and nerve function, fluid balance, acid-base balance, blood pressure regulation, and nutrient metabolism. Adequate potassium intake is essential for these vital functions.
When the body lacks potassium, it can lead to several symptoms indicating the need for potassium supplementation. These symptoms include fatigue, mental fatigue, confusion, constipation, numbness or tingling, muscle symptoms like cramps and spasms, and irregular heartbeat.

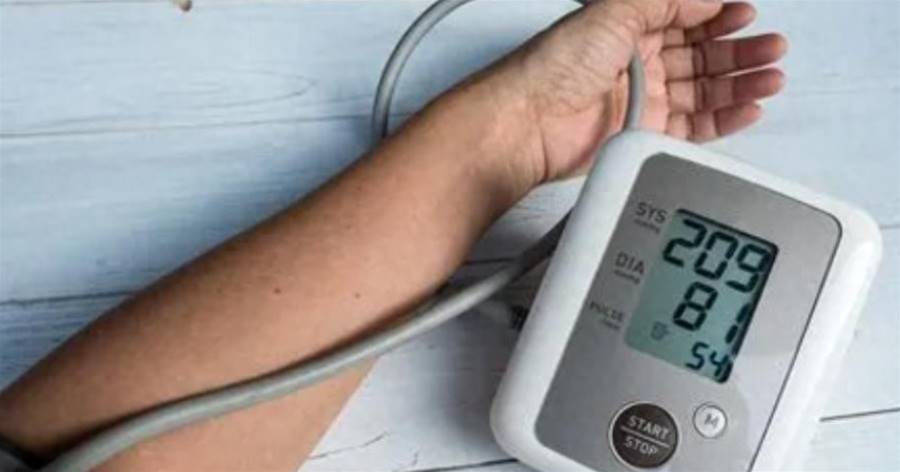
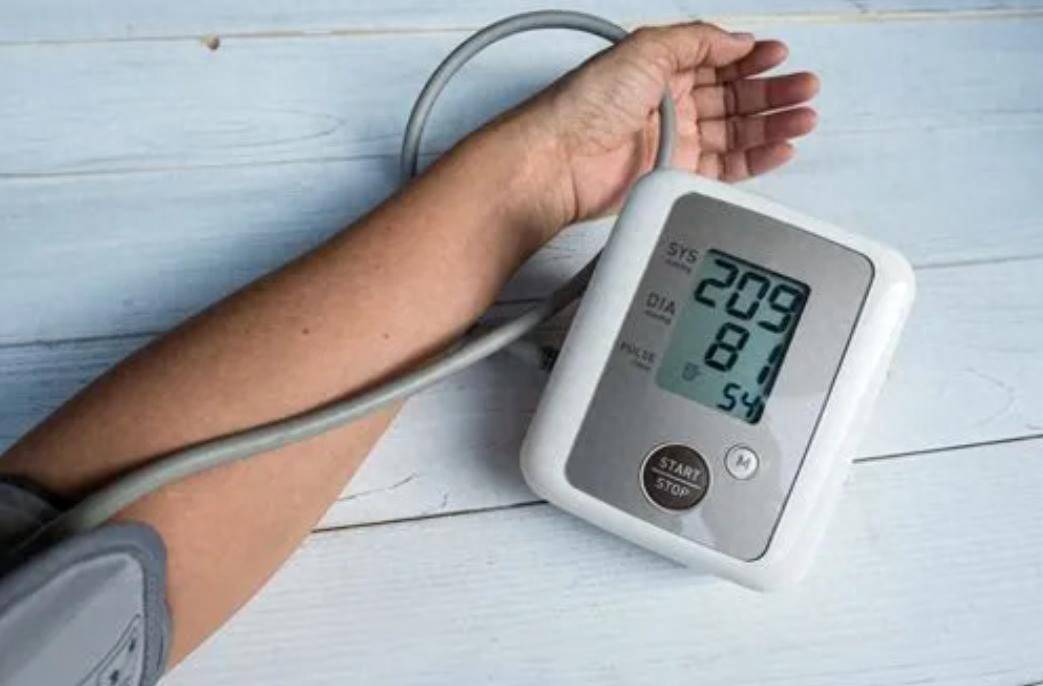
People who take antihypertensive medications may experience low potassium levels due to the effects of these drugs.
Certain medications, such as diuretics, increase urine output and cause the loss of potassium and other electrolytes. Aldosterone receptor antagonists can inhibit the hormone responsible for regulating sodium and potassium balance, leading to potassium depletion. Beta-blockers may also affect potassium balance by reducing aldosterone secretion.

To prevent potassium deficiency, individuals are advised to consume potassium-rich foods. Fruits like bananas, oranges, cantaloupe, and papaya, as well as vegetables like mushrooms and root vegetables, are excellent sources of potassium. Daily potassium intake should range from 2000mg to 3600mg.
In conclusion, maintaining adequate potassium levels in the body is crucial for optimal health. Regular monitoring of potassium levels, consultation with a healthcare professional, and consuming potassium-rich foods can help address potassium deficiencies and promote overall well-being.



















